When we think of farmed animalsA species or specific breed of animal that is raised by humans for the use of their bodies or what comes from their bodies., fishesWhile "fish" is often used to refer to multiple fishes, we use "fishes" to underscore that each fish should be considered as an individual with their own needs, preferences, and abilities, rather than as a monolith consisting of thousands of different species. are often not who comes to mind. However, billions (and more) of fishes are exploited every year between overfishing and aquaculture operations. While fishes are not currently among the resident populations at farmed animal sanctuariesAnimal sanctuaries that primarily care for rescued animals that were farmed by humans., they certainly deserve our consideration. This resource provides information on the plight of farmed fishes, the welfare issues, and discusses fish sentienceThe ability to feel, perceive, or experience things as an individual, especially the ability to feel pleasure and pain..
The Fish Farming Industry
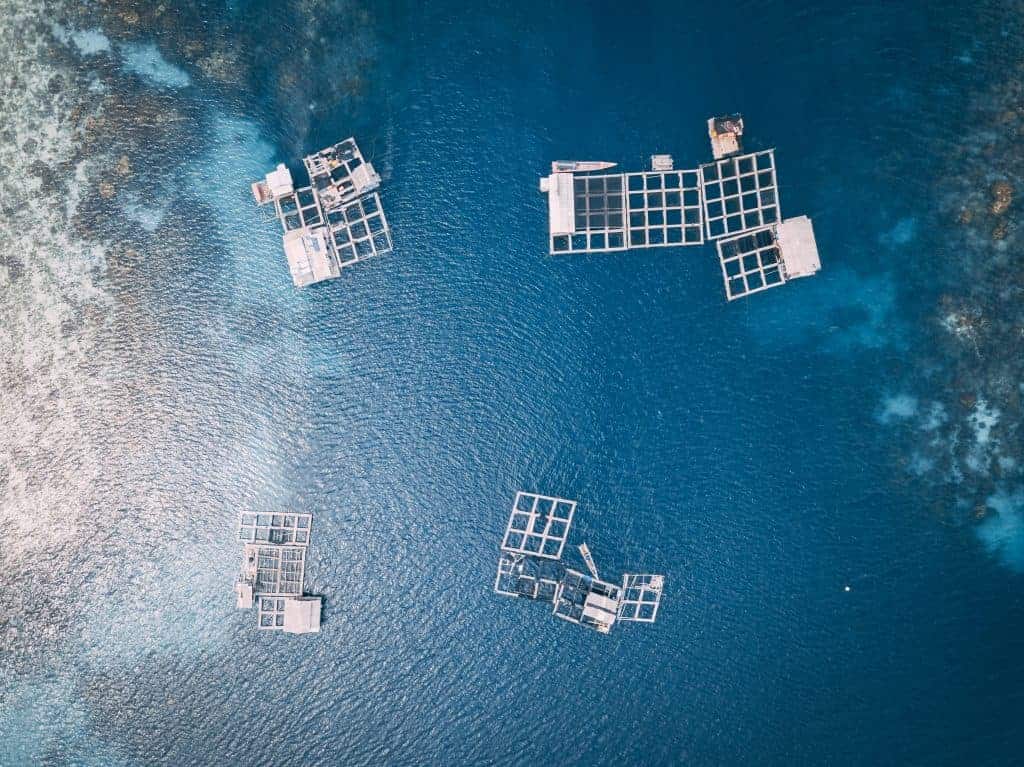
In this form of farming, fishes are raised in enclosures to be sold later as food. These water farmsFor-profit organizations focused on the production and sale of plant and/or animal products. may be mesh cages that are submerged in the ocean or in other natural bodies of water or they may be enclosures made from concrete on land. There are a number of different setups. Regardless of infrastructure, fishes are often overcrowded and suffer from a host of welfare issues.
Commonly farmed fish species are salmon, tuna, cod, trout, and halibut. While the majority of intensively farmed fishes are salmon and trout, other commonly farmed species include catfish, sea bass, carp, and tilapia. Aquaculture is often touted as the solution to the over-fishing of the ocean’s fishes. However, many species that are intensively farmed are fed diets of wild-caught fishes! It can take as much as five pounds of smaller fishes to produce one pound of a fish like salmon or sea bass. Obviously, over-fishing of these smaller species can have a profoundly negative effect on ecosystems.
Some fishes are being genetically altered in an attempt to reduce the incidence of disease and encourage more rapid growth. One study revealed that salmon who are bred and raised in fish factory farmsIntensive agricultural operations that prioritize large volume animal product production using strict production methods, typically away from the public eye. grew at an accelerated rate, causing more than half to go deaf. Other studies have found that salmon raised in intensive farming operations suffer from severe depression, floating lifelessly in their cages.
As you might imagine, overcrowding leads to a lot of poop and uneaten food, which results in water that is high in ammonia and low in oxygen. While the diets of their wild counterparts are varied, intensively farmed fishes receive formulated diets that are simply not as ideal. As in all cases of slaughter, some methods cause terrible suffering. Farmed fishes may be slaughtered by suffocation, cutting gills without stunning, gassing, freezing, and if they are “lucky” stunned first using electricity or blunt strikes to the head.
Fish Sentience
While more and more people are recognizing that mammals are sentient beings, the same consideration has not been given to fishes. Many people still think of fishes as cold, unfeeling automatons, even in the face of evidence to the contrary. Many studies have now shown evidence that fishes are capable of feeling discomfort and pain, in spite of the fact that their bodies are different from mammals. We now know that fishes exhibit a wide variety of sophisticated behaviors. Fishes can develop complex traditions, cooperate with one another, and recognize one another, and some even use tools! They also have excellent long-term memories and have exhibited signs of Machiavellian intelligence (deception). In spite of our differences in brain structure, new evidence suggests that we have more in common than previously thought. Fishes have both a high degree of behavioral plasticity and have compared similarly to other terrestrial vertebrates, including human animals, across a range of intelligence tests.
The Future Of Fish Sanctuaries
While there are a few “petAn animal who spends regular time with humans in their home and life for companionship or human pleasure. Typically a small subset of animal species are considered to be pets by the general public.” fish resources out there, there are not many sanctuaries taking in farmed fishes at this time. For now, you may be able to find information on best practices for above and below ground ponds, transport options, and care practices from The Ohio Fish Rescue or from the Facebook group, Vegans With Fishes.
For more information on the plight of fishes, check out FishFeel.
More To Come!
We are excited to explore more about fish sanctuaries here at The Open Sanctuary Project! If you have information you’d like to share on the topic, please contact us!
SOURCES:
The Welfare of Animals in the Aquaculture Industry | Animal Studies Repository
Rethink Fish | Compassion In World Farming
Fish Farming | Animal Welfare Institute
Fish Intelligence, Sentience and Ethics | Animal Studies Repository