This resource was updated as part of the veterinary review process. It was originally published on January 26, 2023.

Veterinary Review Initiative
This resource has been reviewed for accuracy and clarity by a qualified Doctor of Veterinary Medicine as of May 2023.
Check out more information on our Veterinary Review Initiative here!
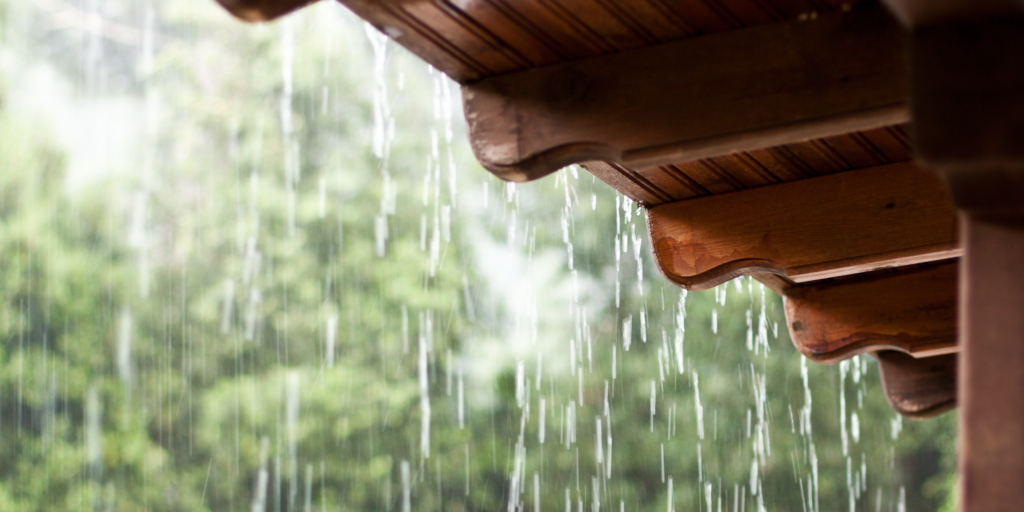
Depending on your sanctuary’s location, you may experience frequent or seasonally rainy, damp, or humid conditions. You may struggle to keep living areas and residents dry during these times. Persistently damp conditions can cause various care issues, from maintenance, safety, and logistics issues on the sanctuary grounds to actual health conditions among residents. One health issue associated with wet climates among equine, ruminant, and camelid residents is rain scald, also called rain rot. If you are in an area with wet weather, learning to identify and, ideally, prevent rain rot is essential, as is knowing how to care for residents who develop this treatable condition properly. This resource defines rain rot and looks at risk factors, how different species are affected, and how to identify rain scald and care for affected residents.
What is Rain Scald?
While caring for equine, camelid, or ruminant residents, you may have encountered terms such as rain scald, rain rot, lumpy wool, strawberry hoof rot, mud fever, or greasy heel. These are all colloquial terms for similar issues caused by the same bacteria, though some refer specifically to the affected areas of the body. So what exactly is rain rot? Rain rot develops when a dormant bacteria living on the skin’s surface, Dermatophilus congolensia, is activated by moisture and enters through tiny breaks in the skin. Something as small as a fly bite is enough to allow the bacteria to enter the skin’s surface and cause an infection. Your veterinarian may refer to this condition as dermatophilosis.

While we are still determining its natural environment, researchers believe it may live naturally in the soil but attempts to isolate it have yet to be successful. It is an infectious condition that can be spread through direct contact with an infected resident or with objects (fence posts, blankets, brushes, food bowls, etc.) the infected individual has touched. It may also spread through insects biting an infected resident and then others.
Signs Of Rain Scald
Rain scald has a pretty distinct set of characteristics. You might see more or less of these signs depending on the severity of the condition. It is important to note that other skin conditions cause some similar symptoms, and it is important to have a qualified veterinarian diagnose the issue before attempting treatment.
- Coarse, tufted coat
- Scabby lesions
- Mats of hair that look like the head of a paintbrush in horses and cowsWhile "cows" can be defined to refer exclusively to female cattle, at The Open Sanctuary Project we refer to domesticated cattle of all ages and sexes as "cows." (Pyramid mats of wool and scabs are seen in sheep)
- Hair loss
- Flaky skin
- Swelling
- Inflamed skin
- Oozing pus
- Bloody, raw skin
Risk Factors

While high humidity and a wet climate are obvious risk factors, several other factors can increase the risk of an individual getting rain scald. Let’s take a look at some of them:
- High humidity
- High temperatures and dampness
- Wet climate
- Flies
- Ectoparasites
- Lack of access to dry shelter and dry ground
- “Unattended” or improper blanketing (sweating under a blanket or wearing a damp blanket)
- Health status (immunocompromised)
Rain rot can be acute or chronic. In milder cases, it may resolve independently in a few weeks, given the right conditions. However, you should never let it go untreated. Left untreated, the condition can worsen, become a chronic issue, or cause other health problems. Some affected individuals may suffer from chronic infections. This can have a significant impact on their well-being. Not only might they be in pain or uncomfortable, but they will also have to be separated from contact with other residents.
Areas Most Commonly Affected
Rain scald can develop anywhere on the body, and individuals might have fifty percent or more of their bodies covered in severe cases. However, most cases are not so severe and are limited to specific areas. Different species may more commonly present with dermatophilosis in different areas of their bodies.
ZoonosisAny disease or illness that can be spread between nonhuman animals and humans. Alert!
When caring for a resident with rain scald, caregivers must use gloves and, ideally, full disposable protective wear. Failure to use protective barriers increases the risk of contracting dermatophilosis. Trust us, you don’t want it! Dispose of any gloves or protective wear used during contact with the affected resident and thoroughly wash up after contact for added protection for you and other residents.
Horses
- Back
- Rump
- Neck
- Top of head
- Sometimes lower limbs
Donkeys
- Shoulders
- Back
- Rump
- Lower limbs (referred to as mud fever)
Cows
- Muzzle
- Tips of ears
- Shoulders
- Withers
- Back
- Rump
- Udder/scrotum
- Lower limbs
- Sides
- Face
- Ears
- Back
- Withers
- Udders
- Lower limbs (strawberry hoof rot)
Goat
- Nose
- Ears
- Lower limbs
- Back
Alpacas/Llamas
- Back
- Neck
- Ears
- Rump
- Feet
Diagnosis
Call Your Veterinarian!
Your veterinarian can often diagnose this disease from the clinical signs combined with environment and weather. They may make a smear from affected skin to evaluate it under a microscope for diagnosis. Your veterinarian can recommend the best course of treatment, which may include prescription antibiotics in severe cases.
Immediate Steps
While you should always contact your veterinarian if you suspect rain scald, there are several things you can do immediately upon noticing the issue, and can be done while you are waiting for your veterinary appointment.
- Get them somewhere dry and well-ventilated.
- Keep the skin dry (watch for sweating or humidity underneath stable blankets)
- If you suspect rain rot, separate them from other residents.
- Do a thorough inspection of their skin, paying particular attention to the most common sites as outlined above. (wear gloves!)
- Check other residents for signs.
- Remove any items (blankets, brushes, bowls) they have come into contact with.
Treatment
Depending on the species and severity of the infection, your veterinarian may advise you to carry out different treatments. If the infection is severe, they may recommend oral or injectable antibiotics. You should also know that there is no completely effective treatment, particularly for severe cases. Treatments are aimed at improving symptoms and controlling disease, but may not 100% eradicate it for severe cases. Generally, treatment involves the following:
- Keeping them dry! (by far the most effective treatment, and may involve bringing the individual indoors)
- Clearing away loose hair and scabs (gently)
- Cleaning the area with chlorhexidine or something similar
- Applying topical antibiotics or powders
- Injections of anti-inflammatories (as prescribed by your veterinarian) may improve well-being of the individual in some cases
Protecting Other Residents
In addition to isolating residents with rain scald, it is important to thoroughly clean and disinfect any surfaces the individual came in contact with. This is difficult and even impossible in some situations, but where possible, do your best. Remove any brushes, halters, blankets, or other items the resident has been in contact with, put them in a plastic bag away from others, and thoroughly wash and disinfect them. If possible, schedule caregivers to enter the afflicted resident’s area last or have a specific caregiverSomeone who provides daily care, specifically for animal residents at an animal sanctuary, shelter, or rescue. assigned to their care. This can prevent cross-contamination that might result in the spreading of bacteria. Always use disposable gloves and put them in an isolation-designated trash can and remove the trash daily, taking care to never cause it to be in contact with equipment that might result in cross-contamination. In addition to these precautions, disposable protective suits and boot covers can further prevent the spread of the bacteria to other residents.
Prevention

The best prevention is to ensure residents have constructed shelters, stay dry during rainy seasons, and have access to the ground where there isn’t standing water or deep mud. Other preventative measures include keeping infected residents and contaminated items away from other residents and providing susceptible residents with waterproof coats if they are to be outside. Care must be taken to ensure they are not sweating under their coats. This can also cause the bacteria to become active.
We hope you have found this resource helpful! Rainy weather can make resident care more challenging. Rain scald can be tricky, but prevention and early treatment are possible. Knowing how to prevent and identify signs of infection and care for affected residents will help you be ready to provide the best care possible.
Infographic
Looking for an easy way to share rain scald prevention and care tips? Check out our infographic here!
SOURCES
Rain Rot | Total Equine Veterinary Associates
Care Of Donkeys Through Winter | The Donkey Sanctuary
Lumpy Wool – A Skin Disease Of Sheep | State Of New South Wales
Disorders Of Skin In New World Camelids | International Journal Of Camel Science
Non-Compassionate Source?
If a source includes the (Non-Compassionate Source) tag, it means that we do not endorse that particular source’s views about animals, even if some of their insights are valuable from a care perspective. See a more detailed explanation here.